Yes, chicken breast is healthy. It’s a lean protein source low in fat and calories, making it ideal for muscle growth and weight loss. Packed with essential nutrients, it supports heart health and overall well-being—especially when grilled or baked without processed additives.
KumDi.com
Is chicken breast healthy? In 2025, nutritionists continue to highlight skinless chicken breast as one of the best lean protein options available. It’s low in saturated fat, rich in essential amino acids, and versatile for a balanced diet. But is it right for everyone? Let’s dive into the science.
Just how healthy is chicken breast? A 3-ounce serving of skinless cooked chicken breast has only 128 calories but packs 26 grams of protein. People recommend chicken breast as their go-to protein source, and with good reason too. This lean meat contains almost no carbs and just 3 grams of fat per serving, making it one of the leanest protein sources you can find.
The benefits of chicken breast go well beyond its protein content. This versatile meat delivers key nutrients like selenium, phosphorus, vitamin B6, and niacin. Chicken breast really shines especially when you have weight management goals. Research shows that eating more protein helps people lose weight more effectively. Your heart benefits from chicken breast’s low saturated fat content, and it might even lower your risk of type 2 diabetes – a condition that affects around 462 million people worldwide.
This piece will get into the science behind chicken breast’s nutritional value. You’ll discover its full potential health benefits and learn practical ways to add more of it to your daily meals for the best results.
Table of Contents
What Makes Chicken Breast a Popular Choice?
Chicken breast has become the most popular cut of poultry, and with good reason too. Its exceptional nutrition and cooking flexibility make it a protein powerhouse. Let’s take a closer look at what makes it so special.
Lean white meat with low fat content
Chicken breast’s nutritional profile stands out, especially if you want to watch your calories and fat intake. A 3-ounce serving of boneless, skinless chicken breast packs just 128 calories while delivering 26 grams of protein. Protein makes up about 80% of these calories, while fat accounts for only 20%.
This lean meat proves to be an excellent choice if you’re watching your weight. Each 3-ounce serving contains less than 3 grams of fat, including just 1 gram of saturated fat per 3.5-ounce portion. The nutrition facts show zero carbohydrates and zero sugar, making chicken breast perfect for various diet plans.
Chicken breast’s lean nature makes it different from other cuts. It has nowhere near the saturated fat found in chicken thighs, legs, and wings. One 3.5-ounce serving provides about 165 calories and 31 grams of protein – a protein-to-calorie ratio that very few whole foods can match.
Versatile and easy to cook
The kitchen possibilities with chicken breast go well beyond its nutritional benefits. It works like a blank canvas that takes on whatever flavors you add. You can prepare it in countless ways:
- Grilling over rice or with vegetables
- Shredding for salads or sandwiches
- Substituting for beef in burgers
- Tossing with pasta and sauce
- Wrapping with salsa and hummus
Cooking methods vary widely too. Chicken breast works well with grilling, baking, roasting, sautéing, broiling, braising, or even poaching. This flexibility combined with quick cooking time makes it perfect for busy weeknight meals.
There’s another reason for chicken breast’s popularity – its mild flavor and tender texture. Unlike stronger-tasting proteins, it doesn’t overwhelm other ingredients but goes together with any seasonings and side dishes you choose. Families love it because it can satisfy different taste priorities.
Common in many healthy diets
Many popular dietary approaches feature chicken breast prominently. This nutrient-dense, lean protein blends naturally into everything from Mediterranean diets to high-protein meal plans. People managing their weight or building muscle find it particularly valuable because of its high-quality protein and minimal fat content.
Chicken breast serves as the healthiest poultry option for those cutting back on red meat. Health experts recommend it as a heart-friendly protein source because it contains little saturated fat – the type linked to high cholesterol and heart disease risk factors.
The benefits go beyond just protein and fat content. Chicken breast provides essential nutrients like selenium, phosphorus, vitamin B6, and niacin, supporting overall nutrition. These qualities explain why you’ll find it in so many healthy recipes for weight management and wellness.
Health experts suggest using lower-fat cooking methods like baking, grilling, poaching, or air frying instead of deep-frying or using too much added fat to get the most health benefits from chicken breast.
Chicken Breast Nutrition Facts Explained
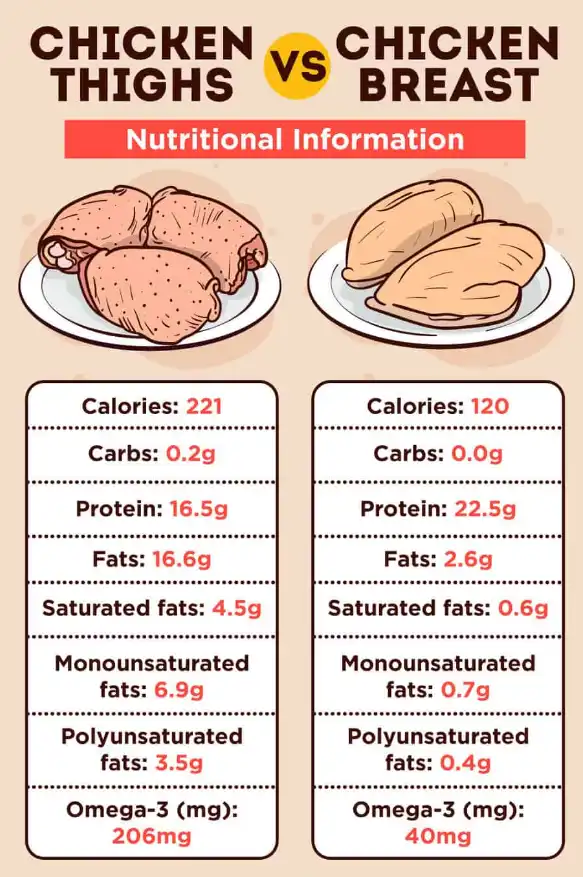
The nutritional makeup of chicken breast shows why people rate it as one of the healthiest protein sources around. Let’s look at what makes this lean meat so good for you and see how different cooking methods change its health benefits.
Calories, protein, and fat breakdown
Chicken breast’s nutritional profile explains why health-conscious people love it as their protein choice. A standard 3.5-ounce (100g) serving of boneless, skinless chicken breast has about 165 calories. This makes it a low-calorie option compared to other proteins. Protein accounts for about 80% of these calories, which is remarkable.
The same 3.5-ounce portion gives you 31 grams of protein. Chicken breast packs a lot of protein – about 9 grams per ounce. A single 6-ounce chicken breast provides around 54.5 grams of protein. That’s about 109% of what you need daily.
Skinless chicken breast has very little fat – just 3.6 grams per 3.5-ounce serving, and only 1 gram is saturated fat. The best part? Chicken breast has zero carbohydrates, so it fits perfectly into low-carb and keto diets. You’ll get about 85mg of cholesterol per 3.5-ounce serving, which is 28% of your daily recommended intake.
Key vitamins and minerals
Chicken breast doesn’t just give you great macros – it’s loaded with essential micronutrients too. Here’s what you’ll find:
- B vitamins – A 6-ounce serving gives you almost 100% of your daily niacin (vitamin B3) needs. You also get plenty of vitamin B6 (92% DV per 6oz) and pantothenic acid (54% DV per 6oz). These vitamins help fight tiredness and fatigue.
- Minerals – A 6-ounce serving packs about 99% of your daily selenium needs. You’ll also get phosphorus (33% DV), magnesium (13% DV), potassium (12% DV), and zinc (15% DV).
Iron content sits at about 1mg per 3.5-ounce serving (6% DV). Chicken breast also gives you choline (36% DV per 6oz), which your brain needs to stay healthy and develop properly.
How skin and cooking method affect nutrition
Skin changes everything about chicken breast’s nutrition. While skinless chicken breast has 165 calories and 3.6 grams of fat per 3.5 ounces, adding skin pushes it to 197 calories and 7.8 grams of fat. The skin almost doubles the fat while reducing the protein percentage.
Your cooking method can really change chicken breast’s nutritional value. Grilling and roasting let fat drip away and keep the meat lean. Deep-frying adds lots of calories and fat.
The best ways to cook chicken breast and keep its nutrients:
- Steaming keeps the meat moist and tender without losing nutrients
- Pressure cooking takes less time and might create fewer unhealthy compounds
- Baking or roasting skinless chicken breast builds flavor while staying lean
Microwaving keeps all the protein intact, so it’s quick and still nutritious. Pressure cooking might help reduce cholesterol oxidation, which is good news if you watch your heart health.
The way you cook your chicken breast determines its final nutrition. Taking the skin off before cooking and using less added fat helps keep it one of the leanest, most nutritious proteins you can eat.
Top 5 Health Benefits of Chicken Breast
Chicken breast packs an impressive nutritional punch and brings several health benefits that make it a great addition to a balanced diet. Science backs up these top five ways this lean protein can boost your body’s health:
1. Supports muscle growth and repair
The quality protein in chicken breast contains essential amino acids that are vital for building and repairing muscle tissue. A 3-ounce serving gives your body all the amino acids it needs for muscle development. Chicken breast stands out with its high leucine content, an amino acid that triggers muscle growth.
Chicken breast delivers more than just protein – it’s rich in B vitamins that power your muscle function. The niacin (B3) and vitamin B6 help your body work efficiently during exercise. These nutrients turn proteins, fats, and carbohydrates into energy you can use, which helps boost your workout performance and recovery.
2. Helps with weight management
The protein-rich nature of chicken breast keeps you satisfied longer, even when you eat fewer calories. This fullness makes it easier to maintain a calorie deficit when you want to lose weight. The protein also helps protect lean muscle mass during weight loss, which keeps your metabolism healthy.
Your body works harder to digest protein compared to fats and carbohydrates. This means you burn more calories processing protein than other nutrients—a plus for anyone watching their weight.
3. Promotes heart health
Chicken breast supports your heart’s health through its low saturated fat content. This minimal fat profile helps lower your body’s cholesterol levels, which reduces heart disease risk.
Research shows eating lots of poultry doesn’t hurt cardiovascular health. Switching from fatty red meats to chicken breast might even lead to better blood pressure levels, giving your heart extra support.
4. May reduce risk of type 2 diabetes
Scientists have found an interesting link between eating chicken breast and lower type 2 diabetes risk. Studies suggest that choosing poultry over processed red meat connects to reduced type 2 diabetes risk. This matters because this condition affects about 462 million people worldwide.
In spite of that, cooking methods play a role. High-heat cooking like grilling and roasting might increase diabetes risk. Gentler cooking methods could be a better choice.
5. Boosts mood and sleep quality
Chicken breast contains tryptophan, an amino acid that affects both mood and sleep patterns. Your body uses tryptophan to make serotonin, the “feel-good hormone”. This brain chemical helps regulate mood and creates feelings of well-being.
The tryptophan in chicken breast also supports better sleep because your body uses serotonin to create melatonin, which controls sleep cycles. Studies show that foods rich in tryptophan might help people drift off faster and sleep better through the night.
How Cooking Methods Impact Healthiness

Your chicken breast’s health benefits depend on how you cook it. Different cooking methods can change its nutritional value by a lot and affect how healthy it ends up on your plate.
Grilled vs. fried vs. baked
Popular cooking methods show striking differences in nutritional value. Air frying gives you crispy chicken with 90% less fat than deep frying. This makes it a healthier choice that tastes just as good. Fried chicken tastes delicious but packs more calories and fat. A 3.5-ounce portion of grilled chicken breast has about 165 calories, while the same fried portion contains around 250 calories or more.
Chicken breast turns out juicier when you bake it at high temperatures (450°F) for about 20 minutes instead of moderate heat (350°F) for longer. Grilled chicken comes with another benefit – excess fat drips off during grilling. This makes it a leaner, lower-calorie option.
Best practices for retaining nutrients
Some cooking methods keep chicken breast’s nutritional value better than others. Stir-frying stands out as one of the healthiest options. It keeps most nutrients while keeping fat content low. Research shows that high-temperature cooking like barbecuing, grilling, and charring can create harmful compounds. These include heterocyclic aromatic amines (HAAs), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and advanced glycation end products (AGEs).
Here’s how to minimize these compounds and get the most nutrition:
- Cook chicken just until it hits 165°F internal temperature
- Let chicken rest 5-10 minutes before cutting so juices redistribute
- Try sous vide, steaming, or pressure cooking for better results
- Start chicken in the microwave before finishing with another method
Avoiding added fats and sodium
Store-bought chicken often has “hidden sodium” from salt solution injections. That’s why you should always check nutrition labels when buying chicken breast.
Ready-made chicken usually has high sodium, but you can control this by:
- Adding flavor with herbs, spices, and citrus instead of salt
- Choosing low-sodium seasonings and marinades
- Adding fresh lemon juice for taste without sodium
- Staying away from high-fat, high-sodium sauces, breadings, and marinades
Chicken breast can lose its nutritional value if you’re not careful with cooking methods. Poaching, roasting, grilling, and steaming add minimal fat and work best for healthy cooking.
What to Watch Out For When Eating Chicken Breast
Chicken breast has many health benefits, but you should know what to watch out for to get the most out of it safely. This healthy food needs proper handling and the right portions to help you reach your health goals.
Portion control and cholesterol
The right portion size is vital when eating chicken breast. One serving should be about 3-3.5 ounces – about half of a large chicken breast or the size of your palm. This amount gives you enough protein without too many calories if you’re watching your weight.
Chicken breast has less cholesterol than other cuts, but it still contains some. A 100-gram portion of skinless chicken breast has about 73 milligrams of cholesterol. The amount is low, but if you have heart issues, the American Heart Association suggests limiting your portion to 3 ounces.
Food safety and proper storage
You need to handle raw chicken carefully to avoid getting sick. Harmful bacteria like Salmonella and Campylobacter are common in raw poultry and can make you very ill. Safe handling is not optional.
Here are the safety rules you must follow:
- Keep raw chicken at 38-40°F in your fridge and use it within 1-2 days of buying it
- Put raw chicken on the bottom shelf of your fridge on a plate so it doesn’t drip
- Cook chicken until it reaches 165°F inside to kill harmful bacteria
- Don’t wash raw chicken as this spreads bacteria around
- Put leftover chicken in the fridge within 2 hours after cooking
Allergies and dietary restrictions
Chicken allergies aren’t common, but they do happen. Signs can be mild like itchy skin and runny nose, or severe like trouble breathing and anaphylaxis. People who are allergic to chicken might also react to turkey, goose, and duck.
Some people are allergic to raw chicken but can eat it cooked. On top of that, if you have kidney disease, you should be careful with high-protein foods like chicken breast and talk to your doctor about how much you can eat.
Taking the skin off before cooking makes a big difference in fat content. Skinless white meat chicken, especially breast, has less cholesterol and saturated fat than other cuts, which makes it a good choice for most restricted diets.
Conclusion
Chicken breast ranks among the best protein sources you can find. It’s definitely worth its status as a dietary staple. This piece showed how a 3-ounce serving packs 26 grams of protein with minimal fat and zero carbs. The benefits go way beyond the reach and influence of just protein content. This lean meat gives you essential micronutrients like selenium, B vitamins, and phosphorus that boost your overall wellness.
You’ll love chicken breast’s adaptability in everyday meals. This protein works great in countless recipes – grill it, bake it, steam it, or air-fry it. Your cooking method affects its nutrition by a lot, but chicken breast stays healthy when you cook it right. Just watch those added fats and sodium.
Safe food handling is crucial with chicken. Store it properly, cook it to 165°F, and handle it carefully. These steps prevent foodborne illness and help you get all the benefits from this protein powerhouse. Portion control matters too, even with lean meats like chicken breast, especially when you have to watch your cholesterol.
Chicken breast belongs at the heart of a balanced diet. Research backs its benefits for muscle growth, weight control, heart health, and mood balance. It fits most eating patterns perfectly. No single food creates a healthy diet, but chicken breast gives you a great foundation. You can build nutritious, filling meals that help reach your health goals.

FAQs
Is chicken breast good for weight loss?
Yes, chicken breast is good for weight loss because it’s high in protein and low in calories. This combination helps preserve lean muscle mass while promoting fat loss.
What are the main chicken breast nutrition facts?
Chicken breast contains approximately 165 calories, 31g of protein, and 3.6g of fat per 100g serving. It’s rich in niacin, selenium, and vitamin B6.
Is grilled chicken breast healthier than fried?
Yes, grilled chicken breast is healthier. Grilling retains nutrients and minimizes added fats compared to frying, which increases calorie content with oils and breading.
Can eating chicken breast every day be unhealthy?
Eating chicken breast daily is generally healthy if it’s cooked properly and part of a balanced diet. However, variety is key to getting a full range of nutrients.
What are the benefits of eating chicken breast?
Benefits include improved muscle repair, weight management, heart health, and better metabolism. Its lean protein supports active lifestyles and long-term wellness.





