The global birth rate decline is causing major demographic shifts, including aging populations and labor shortages. These changes impact economies, healthcare systems, and long-term social structures around the world.
KumDi.com
The global birth rate decline is transforming societies at an unprecedented pace. With fewer babies being born in countries across the globe, nations are now facing aging populations, shrinking workforces, and economic uncertainty. This article explores the root causes, real-world consequences, and potential solutions to this demographic challenge.
As we navigate through the complexities of modern society, one of the most pressing issues facing nations worldwide is the significant decline in birth rates. This phenomenon is not confined to a single region; rather, it spans across continents, affecting both developed and developing countries. The implications of this trend are profound, influencing economic stability, social structures, and the future workforce. In this article, we will explore the multifaceted reasons behind declining birth rates, the consequences for societies, and potential solutions to address this demographic challenge.
Table of Contents
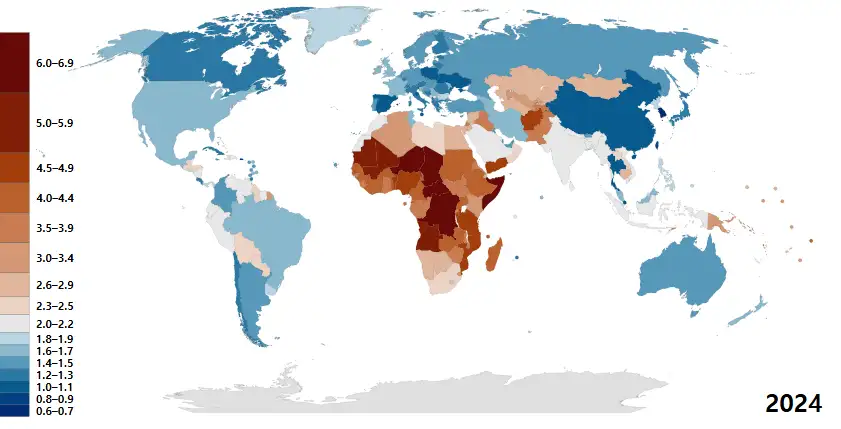
Understanding the Decline in Birth Rates
Historical Context
Over the past several decades, the global birth rate has experienced a dramatic decline. In the 1960s, the average number of births per woman was approximately 5.1. Fast forward to today, and that number has plummeted to around 2.4. This shift is particularly evident in countries like Italy, South Korea, and Japan, where projections indicate that populations could be halved within the next 75 years. Understanding the historical context of these changes is crucial for grasping their current implications.
Factors Contributing to Lower Fertility Rates
Several factors contribute to the declining birth rates observed globally:
- Economic Considerations: As countries develop economically, the cost of raising children often becomes a significant deterrent. Families face rising expenses related to housing, education, and healthcare, leading many to postpone or forgo having children altogether.
- Cultural Shifts: Changing societal norms and values have led to a greater emphasis on individualism and career advancement. Many couples prioritize their professional lives, resulting in delayed parenthood.
- Access to Contraception: Improved access to family planning resources has empowered individuals to make informed choices about reproduction. While this is a positive development, it has also contributed to lower birth rates.
- Educational Attainment: Higher levels of education, particularly among women, correlate with reduced fertility rates. As women pursue higher education and career opportunities, they often choose to have children later in life.
The Economic Implications of Declining Birth Rates
Aging Populations and Workforce Shortages
One of the most immediate concerns stemming from declining birth rates is the aging population. As birth rates decrease, the proportion of older individuals in society increases. This shift creates a significant imbalance in the workforce, leading to potential labor shortages. For instance, the old-age dependency ratio (OADR) has risen dramatically, indicating that fewer workers are available to support a growing number of retirees.
Strain on Social Services
With an aging population comes increased demand for social services, particularly healthcare and pensions. Countries like the United Kingdom and the United States are already grappling with the financial implications of supporting a larger elderly demographic. As the number of retirees grows, the burden on social security systems intensifies, raising concerns about sustainability.
Economic Growth Challenges
Declining birth rates can hinder economic growth. A shrinking workforce may lead to decreased productivity and innovation, ultimately affecting a nation’s competitiveness on the global stage. Governments must consider strategies to mitigate these challenges and ensure a stable economic future.
Societal Consequences of Fewer Births

Changing Family Structures
The decline in birth rates has led to evolving family dynamics. Smaller family units are becoming the norm, which can impact social cohesion and community support systems. As families become more nuclear, the traditional extended family structure may weaken, leading to increased isolation for some individuals.
Cultural Shifts in Parenting
With fewer children being born, parenting styles and expectations are also changing. Parents may feel increased pressure to provide exceptional opportunities for their children, leading to heightened competition and stress. This shift can affect children’s mental health and overall well-being.
Impacts on Education Systems
As birth rates decline, educational institutions may face challenges related to enrollment and funding. Schools may need to adapt to changing demographics, potentially leading to school closures or consolidations in areas with declining populations.
Global Perspectives on Birth Rate Declines
Developed vs. Developing Nations
While the decline in birth rates is a global issue, its manifestations differ between developed and developing nations. In wealthier countries, lower fertility rates often stem from lifestyle choices and economic factors. Conversely, in developing nations, high fertility rates may persist due to cultural norms and limited access to education and healthcare.
Immigration as a Solution
Many developed countries are turning to immigration as a potential solution to labor shortages caused by declining birth rates. By welcoming immigrants, nations can bolster their workforce and maintain economic stability. However, this approach raises questions about integration, cultural identity, and long-term sustainability.
Strategies to Address Declining Birth Rates
Pro-Natalist Policies
Governments are exploring various strategies to encourage higher birth rates. Pro-natalist policies, which incentivize families to have more children, are gaining traction. These may include:
- Financial Incentives: Tax breaks, direct payments, and subsidies for childcare can alleviate the financial burden of raising children.
- Parental Leave Policies: Expanding parental leave options allows parents to balance work and family life more effectively.
- Affordable Childcare: Increasing access to affordable childcare services can encourage couples to have more children.
Education and Awareness Campaigns
Raising awareness about the importance of family planning and reproductive health is essential. Educational initiatives can empower individuals to make informed choices about parenthood and fertility. Schools and community organizations can play a vital role in disseminating this information.
Support for Work-Life Balance
Creating a supportive environment for working parents is crucial. Employers can implement flexible work arrangements, such as remote work options and flexible hours, to help parents manage their responsibilities. This approach can foster a culture that values family life while maintaining productivity.
The Role of Technology in Family Planning
Advancements in Reproductive Health
Technological advancements in reproductive health are transforming family planning. Innovations such as fertility tracking apps, telemedicine consultations, and improved assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are making it easier for individuals to navigate their reproductive choices.
Addressing Infertility
As birth rates decline, addressing infertility becomes increasingly important. Governments and healthcare systems must prioritize access to fertility treatments and support for individuals facing reproductive challenges. This includes funding for research and development in reproductive health technologies.
The Future of Global Birth Rates
Projections and Trends
Looking ahead, the trajectory of global birth rates remains uncertain. While some countries may experience a resurgence in fertility due to pro-natalist policies, others may continue to face challenges related to declining birth rates. Understanding these trends is essential for policymakers and society as a whole.
The Importance of Collaboration
Addressing the issue of declining birth rates requires collaboration among governments, healthcare providers, and communities. By working together, stakeholders can develop comprehensive strategies that promote family growth while considering the unique needs of each population.
Conclusion
The decline in birth rates is a complex issue with far-reaching implications for societies worldwide. As nations grapple with the challenges posed by aging populations, workforce shortages, and changing family dynamics, it is crucial to explore innovative solutions. By implementing pro-natalist policies, raising awareness about reproductive health, and fostering a supportive environment for families, we can work towards a future that balances economic stability with the joys of parenthood. The path forward requires collaboration, understanding, and a commitment to nurturing the next generation.

FAQs
Why is the global birth rate declining?
The global birth rate decline is driven by factors like urbanization, rising education levels, economic uncertainty, and lifestyle changes. These factors contribute to low fertility rate trends worldwide.
How does a low birth rate affect a country’s economy?
A low birth rate can reduce the working-age population, leading to a shrinking workforce and increased financial pressure on pension and healthcare systems, especially in aging populations.
Which countries are most affected by declining birth rates?
Nations like Japan, South Korea, Italy, and Germany are severely impacted by the global birth rate decline, facing population aging effects and long-term growth challenges.
What are the social impacts of fewer babies being born?
Fewer births mean fewer students in schools, smaller family sizes, and less community engagement, all contributing to societal shifts tied to low fertility rate trends.
Can government policies reverse the birth rate decline?
Pro-natalist policies such as paid parental leave, childcare support, and housing incentives aim to slow the global birth rate decline, though results vary across regions and cultures.




